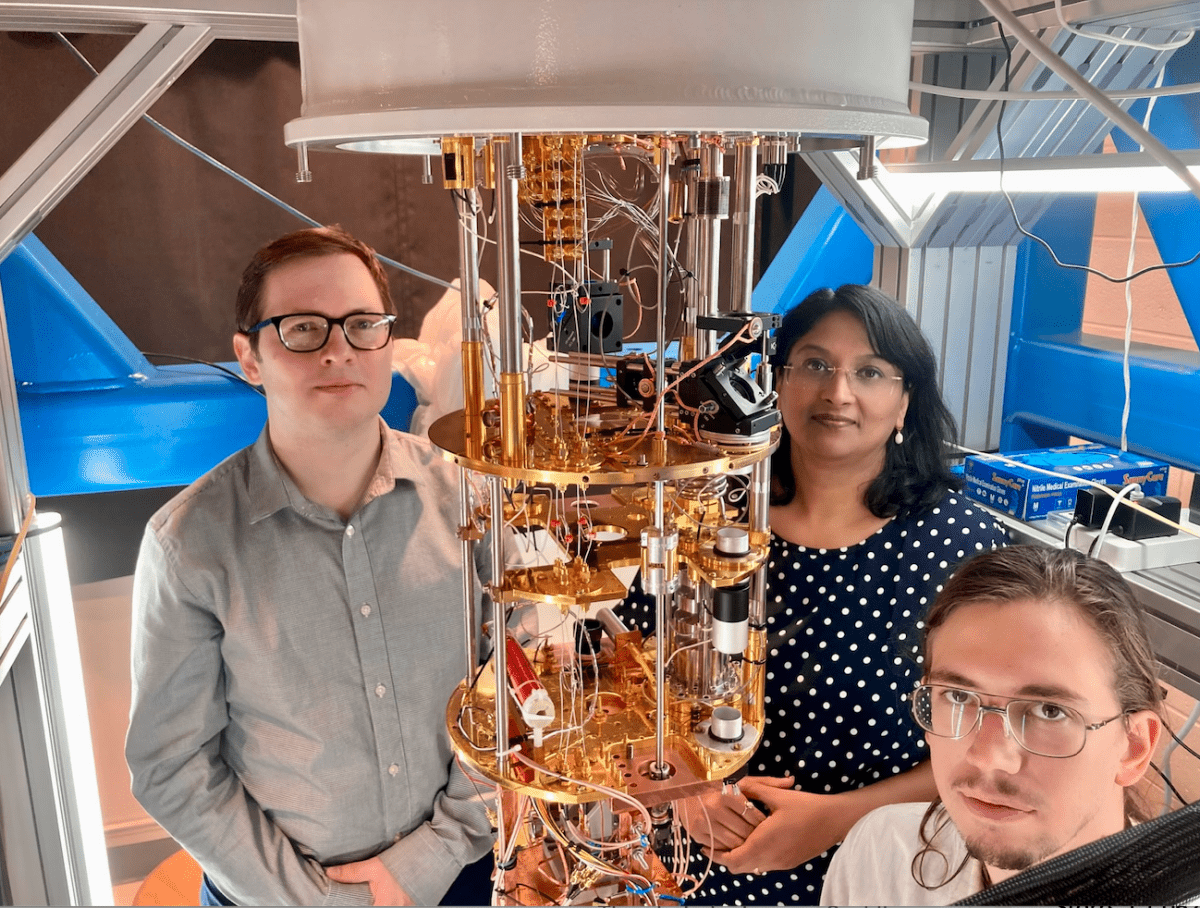
NSF award to Profs. Jain and Sochnikov
Professors Jain and Sochnikov received NSF research grant entitled “New Quantum Elastocaloric Demagnetization Refrigeration for the Millikelvin Range”. A major focus of their research will be the cooling of quantum chips. For this purpose, their teams will study ‘spin liquids’, which can be harnessed to achieve millikelvin temperatures without magnetic fields. At such low temperatures, […]
[Read More]
Prof. Jain is organizing International Workshop on Oxide Electronics
Associate Professor of Physics Menka Jain and the Institute of Materials Science is co-organizing a workshop-28th International Workshop on Oxide Electronics (IWOE) in Maine next month. The IWOE series has become an important venue to discuss recent advances and emerging trends in this developing field. The aim of the workshop is to provide an interdisciplinary […]
[Read More]
Prof. Jonathan Trump Interviews about the James Webb Space Telescope
The James Webb Space Telescope released its first science observations on July 12 with much fanfare and excitement across the globe. UConn Physics Professor Jonathan Trump is part of the Cosmic Evolution Early Release Science collaboration that was awarded some of the first observations on the transformative new space telescope. Prof. Trump was interviewed by several local media outlets, […]
[Read More]
Prof. Cara Battersby Awarded an NSF CAREER grant
Professor Cara Battersby has been awarded an NSF CAREER grant! “The Faculty Early Career Development (CAREER) Program is a Foundation-wide activity that offers the National Science Foundation’s most prestigious awards in support of early-career faculty who have the potential to serve as academic role models in research and education and to lead advances in the […]
[Read More]
Plates that Helped Map the Universe, Now at UConn
UConn is now home to tools that have played an instrumental role in mapping the universe — 10 large aluminum plates used as part of the Sloan Digital Sky Survey (SDSS). Measuring 32 inches across, one-eighth of an inch thick, and with thousands of tiny holes drilled in them, these plates may not be the […]
[Read More]
Two Physicists are in Project Daedalus that Focuses on Materials for Aerospace in New $4.7 Million Contract
UConn’s collaboration with the Department of Defense Air Force Research Laboratory (AFRL) is launching a new project. It is titled Multiscale Modeling and Characterization of Metamaterials, Functional Ceramics and Photonics. This is a $4.7 M contract with $1M for Physics. The project’s goal is to explore and advance the understanding of electronic, photonic, magnetic, and […]
[Read More]
Research of UConn Professor Daniel Angles-Alcazar featured in UConn Today
The article The Largest Suite of Cosmic Simulations for AI Training Is Now Free to Download; Already Spurring Discoveries describe research of a team of astrophysicists that includes UConn Professor of Physics Daniel Anglés-Alcázar. “Machine learning is revolutionizing many areas of science, but it requires a huge amount of data to exploit,” says Anglés-Alcázar. “The […]
[Read More]
Prof. J. Trump interview about the launch of the James Webb telescope
UConn Physics Professor Jonathan Trump is part of a group of scientists who will be the first to conduct research using the James Webb space telescope. The local Fox News TV station conducted an interview with Prof. Trump.
[Read More]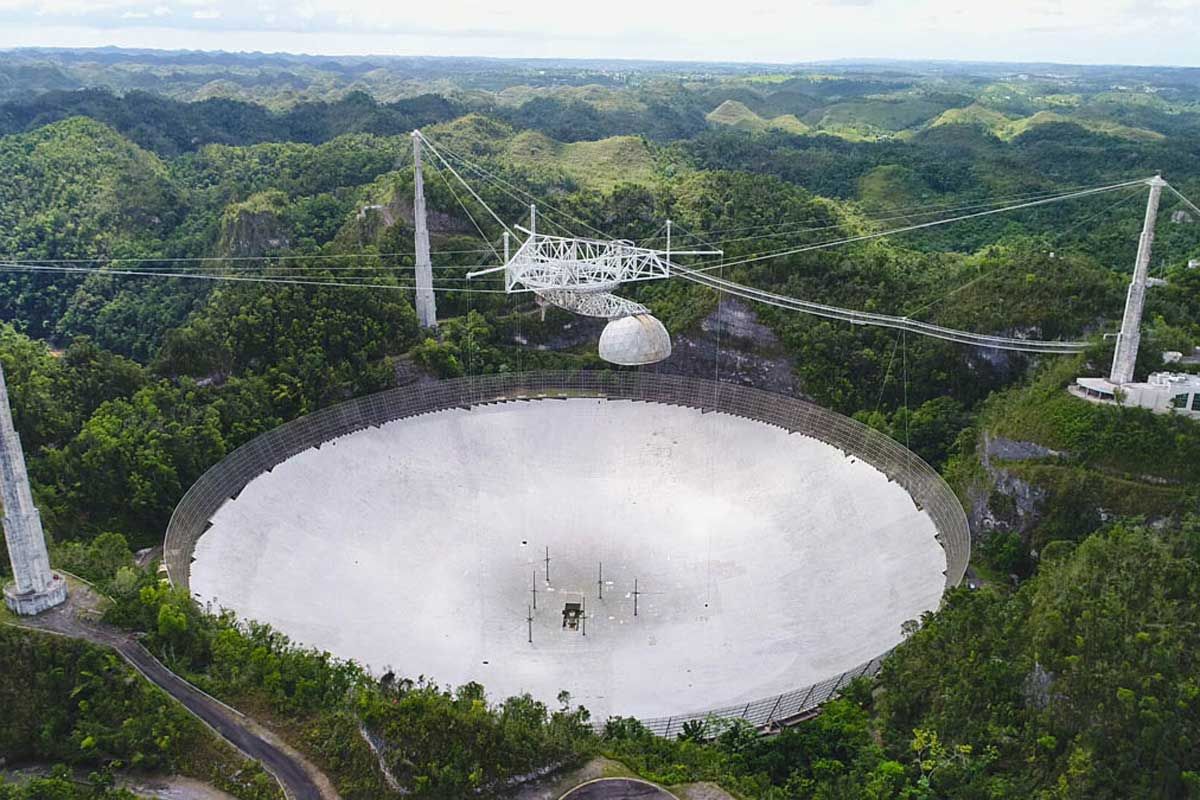
U.S. Senators introduce a resolution to recognize the Arecibo Observatory Telescope
On Friday December 3rd, a group of U.S. Senators, Richard Blumenthal (D-CT), Edward J. Markey (D-MA), Marco Rubio (R-FL), Elizabeth Warren (D-MA), and Rick Scott (R-FL) introduced a bipartisan a resolution to recognize the significant scientific, educational, and economic contributions made by the Arecibo Observatory telescope. “The telescope at Puerto Rico’s Arecibo Observatory was a […]
[Read More]
Prof. Chiara Mingarelli awarded NSF grant
Chiara Mingarelli, Assistant Professor of Physics at UConn, is the lead researcher on a $650,000 Collaborative Research Grant from the National Science Foundation, half of which is earmarked for UConn, to conduct an experiment to prove the existence of supermassive black hole binaries. This grant will combine, for the first time, traditional astronomy with gravitational […]
[Read More]
A Physics Ph.D. Student’s Step-By-Step Journey to Storrs and Distant Galaxies
UConn Physics graduate student Mohammed (Mo) Akhshik works on data gathered using the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) and has led to exciting discoveries, some while he served as the science Principle Investigator of the REQUIEM HST program from which he is co-author on two publications, one in Nature and one in Nature Astronomy. Akhshik is also […]
[Read More]
Professor Daniel Anglés-Alcázar research featured in ‘UConn Today’ and CBC radio interview
At the center of galaxies, like our own Milky Way, lie massive black holes surrounded by spinning gas. Some shine brightly, with a continuous supply of fuel, while others go dormant for millions of years, only to reawaken with a serendipitous influx of gas. It remains largely a mystery how gas flows across the universe […]
[Read More]
Physics alumnus Prof. Douglas Goodman and Professor Emeritus Winthrop Smith Featured in Online Peer Review Journal
Prof. Emeritus Winthrop Smith and former student Prof. Douglas Goodman (Quinnipiac University) Edit Special Issue of Open Access Journal Atoms, on Low Energy Interactions between Ions and Ultracold Atoms The Special Issue of the online journal Atoms is a collection of current peer-reviewed articles by experts in the field of ultracold collisions and reactions involving […]
[Read More]
New Faculty Hire-Dr. Anh-Thu Le
The Physics Department welcomes our newest faculty member, Dr. Anh-Thu Le, although he prefers to be called simply AT. AT worked for many years at the well-known James R. Macdonald Laboratory, rising to the rank of Research Professor. He worked alongside a world-known theorist, Dr. Chii-Dong Lin. Dr. Le went on to become an Assistant […]
[Read More]
Professor Puckett’s Group Prepares New Measurements of “femtoscopic” Neutron Structure at Jefferson Lab
Professor Andrew Puckett’s research group is currently leading, as part of a collaboration of approximately 100 scientists from approximately 30 US and international institutions, the installation in Jefferson Lab’s Experimental Hall A of the first of a series of planned experiments known as the Super BigBite Spectrometer (SBS) Program, with beam to Hall A tentatively […]
[Read More]
Undergraduate Researcher Nicole Khusid featured in UConn Today
Physics major Nicole Khusid, a rising senior at UConn, was featured in a UConn Today article about her research. Nicole has been working on gravitional lensing of distant sources of gravitational waves, seeking to understand their multimessenger signals and detectability by future astrophysics facilities. Nicole was awarded a SURF (Summer Undergraduate Research Fund) award to […]
[Read More]
Standard model challenged by new measurement
It seems that the muon, a heavier partner of the electron, may be breaking what have been understood as the laws of physics. The findings announced on April 7th were met with excitement and speculation at what this might mean. UConn physics researchers Professor Thomas Blum and Assistant Professor Luchang Jin helped pioneer the theoretical physics behind the findings.
[Read More]
Prof. Battersby’s research featured in UConn Today article
Professor Cara Bettersby’s research is featured in the article “The Study of Big Data: How CLAS Researchers Use Data Science” published by UConn Today. Prof. Battersby’s work focuses on describing and studying the center of the Milky Way galaxy, which she calls an “experimental playground” for the distant cosmos. Her work described the spectroscopy of […]
[Read More]
Dr. Yasaman Homayouni featured in CLAS story on 2021 graduates
New Physics PhD graduate Yasaman Homayouni is featured in a story on the class of 2021 from the College of Liberal Arts and Sciences (CLAS). For the full story of what inspired Yasaman and other students during their time at UConn, see the article in UConn Today.
[Read More]
An anomalous moment for the muon
Mark Rayner/CERN The Fermilab E989 experiment announced the first new result on the muon’s anomalous magnetic moment in almost 20 years. The new measurement, combined with Brookhaven’s E821, has increased the discrepancy with the Standard Model value to 4.2 standard deviations. UConn Professors Tom Blum and Luchang Jin explain the theory calculations in a feature […]
[Read More]